Study: Clove essential oil can keep blood sugar levels at bay after eating
12/27/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
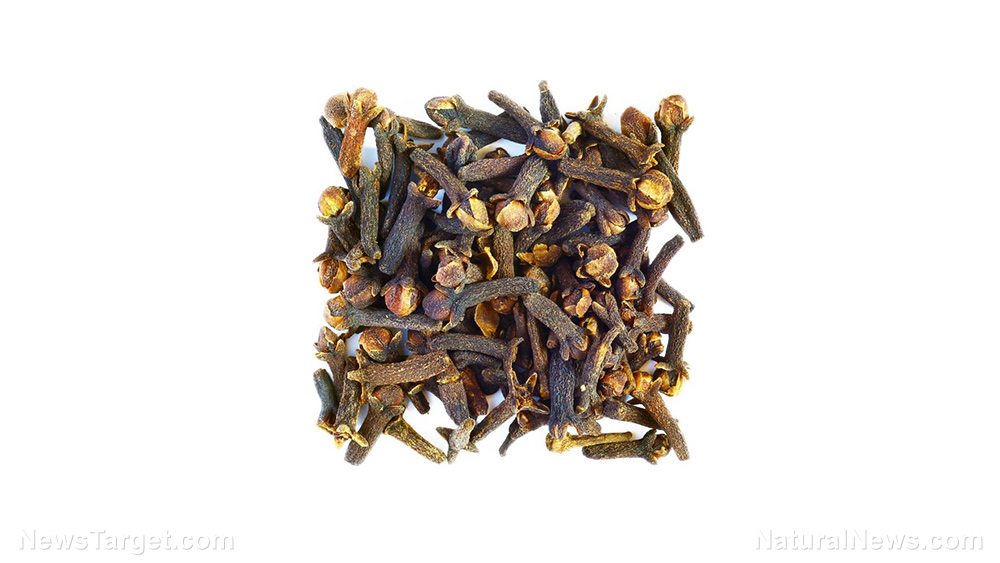

The aromatic flower buds of the Syzygium aromaticum plant known as cloves are common ingredients in many cuisines and in traditional medicine. Besides being a natural antibacterial and having anti-obesity properties, cloves have also been reported to have anti-diabetic properties.
In a study published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, researchers from India and the U.S. conducted a pilot study to determine if the polyphenolic extract from unopened clove buds can influence glucose metabolism. They found that cloves have great potential in the treatment of diabetes as its polyphenol-rich extract can decrease blood glucose levels after a meal.
The effects of clove extracts on preprandial and postprandial blood glucose
Type 2 diabetes is considered a global pandemic and is a huge contributor to the increasing incidence of serious conditions like cardiovascular disease. According to statistics, more than 75 percent of American adults older than 65 suffer — to some extent — from glucose homeostasis dysfunction. Poor diet and food choices, coupled with reduced physical activity, are said to be the main factors responsible for the rise in Type 2 diabetes cases.
Postprandial blood glucose, which is measured two hours after the start of a meal, is a good indicator of the overall status of a person’s glucose homeostasis. Preclinical studies suggest that clove and the active components of its essential oil, namely eugenol and acetyl eugenol, have the ability to regulate pathways involved in glucose homeostasis. In fact, reports have emerged claiming that the polyphenolic extract of unopened clove buds (PCE) can influence liver function, antioxidant status, and alcohol metabolism.
Because of these findings, the researchers hypothesized that, since the liver plays a role in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes, PCE may have a beneficial effect on glucose metabolism. To test this hypothesis, they recruited 13 healthy volunteers and gave them supplements containing 250 milligrams (mg) PCE to be taken once a day for 30 days.
The researchers divided the volunteers into two groups based on their initial preprandial glucose levels. Group I consisted of seven individuals whose glucose levels before meals was 100 mg/deciliter (dL) or less. Group II, on the other hand, consisted of only six individuals with glucose levels between 101 and 125 mg/dL. The researchers also tested the effects of PCE on glucose uptake, liver cell glucose production, and carbohydrate hydrolyzing enzymes in vitro.
The researchers found that PCE supplementation significantly reduced mean postprandial glucose levels in both groups from day 12 until day 30. PCE supplementation also decreased mean preprandial glucose levels in group II at days 24 and 30. Meanwhile, PCE enhanced glucose uptake in L6 myocytes (muscle cells) and inhibited glucose production in Hep62 (liver cancer) cells. In cell-free assays, PCE also inhibited a-amylase and a-glucosidase activities. a-Amylase is the enzyme responsible for converting dietary starch into glucose molecules, while a-glucosidase is needed for the absorption of glucose in the gastrointestinal tract.
Based on these results, the researchers concluded that PCE can help diabetics achieve and maintain healthy glucose metabolism, and its potential needs to be further explored in large-scale clinical trials.
The health benefits of cloves
Cloves are versatile cooking ingredients with potent medicinal properties. Not only are cloves an excellent source of nutrition, but they are also chock-full of antioxidants that help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. Some of the nutrients cloves can provide include fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, calcium, and manganese. Vitamin C, together with vitamin E and eugenol, also serves as a natural antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals. The presence of these nutrients in cloves gives this popular spice the ability to improve overall health.
Besides having anti-diabetic properties, cloves are also known for:
- Improving liver health
- Killing bacteria
- Preventing bone disease
- Preventing ulcers
- Promoting oral health
- Reducing abdominal and liver fat
- Slowing the growth of cancer
Cloves can be used in many ways and offer a variety of health benefits. To make the most out of cloves, incorporate this medicinal spice into your diet by adding it to dishes or by making a warm cup of soothing, pain-relieving clove tea every day. (Related: Discover the astounding healing properties of clove oil.)
Sources include:
BMCComplementAlternMed.BiomedCentral.com
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
anti-diabetes, cloves, food is medicine, natural remedies, phytonutrients, prevention, research, Spices, supplements, Type 2 Diabetes
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 PREVENTDIABETES.NEWS
All content posted on this site is protected under Free Speech. PreventDiabetes.news is not responsible for content written by contributing authors. The information on this site is provided for educational and entertainment purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional advice of any kind. PreventDiabetes.news assumes no responsibility for the use or misuse of this material. All trademarks, registered trademarks and service marks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.